Neurokognition II
SS2025
Sommersemester 2025
| Vorlesung: | Dienstag, | 13.30 - 15.00, A10.204 (1/204) | (O. Maith) |
| Übung (Englisch): | Mittwoch, | 11.30 - 13.30, A11.202 (1/B202) | (O. Maith) |
| Übung (Englisch): | Mittwoch, | 13.45 - 15.15, A11.202 (1/B202) | (V. Forch) |
Information
Exercises start on April 16th, registration on OPAL
A detailed schedule for lecture and exercise topics can be found here.
Inhalte
Die Veranstaltung führt in die Modellierung neurokognitiver Vorgänge des Gehirns ein. Neurokognition ist ein Forschungsfeld, welches an der Schnittstelle zwischen Psychologie, Neurowissenschaft, Informatik und Physik angesiedelt ist. Es dient zum Verständnis des Gehirns auf der einen Seite und der Entwicklung intelligenter adaptiver Systeme auf der anderen Seite. Die Neurokognition II beleuchtet komplexere Modelle von Neuro-psychologischen Prozessen, mit dem Ziel neue Algorithmen für intelligente, kognitive Roboter zu entwickeln. Themen sind Wahrnehmung, Gedächtnis, Handlungskontrolle, Emotionen, Entscheidungen und Raumwahrnehmung. Zum tieferen Verständnis erfordern die Übungen auch praktische Aufgaben am Rechner.
Videos zur Vorlesung befinden sich hier.
Randbedingungen
Empfohlene Voraussetzungen: Grundkenntnisse Mathematik I bis IV, Neurokognition I
Prüfung: Mündliche Prüfung
Ziele: Fachspezifische Kenntnisse der Neurokognition
Lectures
Part I Introduction
The introduction motivates the goals of the course and basic concepts of models. It further explains why computational models are useful to understand the brain and why cognitive computational models can lead to a new approach in modeling truly intelligent agents.
The styles of computation used by biological systems are fundamentally different from those used by conventional computers: biological neural networks process information using energy-efficient, asynchronous, event-driven methods. They learn from their interactions with the environment, and can flexibly produce complex behaviors. These biological abilities yield a potentially attractive alternative to conventional computing strategies.
Neurokognition II is particularly devoted to model perception cognition and behavior in large-scale neural networks. The course introduces models of early vision, attention, object recognition, space perception, cognitive control, memory, emotion and consciousness.
Part I Anatomy
1.1 Anatomy
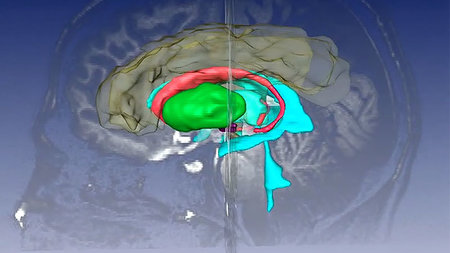
This lecture gives a brief introduction into brain anatomy and provides information about the function of multiple brain areas and nuclei.
Part II Early Vision
Perhaps our most important sensory information about our environment is vision. The lecture "early vision" explains the first processing steps of visual perception.
Overview:Adelson, E. H., Bergen, J R. (1985): Spatiotemporal energy models for the perception of motion. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A. 2:284-299
DeAngelis, G., Ohzawa, I., Freeman, R.D. (1995): Receptive-field dynamics in the central visual pathways. TINS Vol. 18, No. 10, 1995
Vision starts in the retina, which is considered part of the brain. The lecture explains the concept of a receptive field and introduces simple models of early processing that model dynamic receptive fields.
Additional Reading:Cai D, DeAngelis GC, and Freeman RD (1997) Spatiotemporal receptive field organization in the LGN of cats and kittens. J Neurophysiol 78:1045-1061.
Shape perception refers to the fact that the visual system has filters that respond optimally to oriented bars or edges, which takes place in area V1, also called striate cortex. This lecture introduces into the receptive fields of neurons in V1 and explains what kind of information V1 encodes with respect to shape perception.
Color perception starts in the retina, since we have receptors that are selective for different wavelength of the light. This lecture introduces into models of color selective receptive fields.
Seeing in three dimensions requires to extract depth information from the visual scene. One method, called binocular disparity, is of primary focus.
Suggested Reading: Read JCA (2005) Early computational processing in binocular vision and depth perception. Progress in Biophysics and Molecular Biology 87:77-108.
Gain normalization appears to be a canonical neural computation in sensory systems and possibly also in other neural systems. Gain normalization is introduced and examples for normalization in retina, in primary visual cortex, in higher visual cortical areas and in non-visual cortical areas are given.
Suggested Reading: Carandini M., Heeger DJ. (2012) Normalization as a canonical neural computation. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 13:51-62.
Why does the brain develop a particular set of feature detectors for early vision. This lecture addresses how approaches that rely on learning allow to better understand the coding of vision in the brain.
Suggested Reading:
Wiltschut, J., Hamker, F.H. (2009) Efficient Coding correlates with spatial frequency tuning in a model of V1 receptive field organization. Visual Neuroscience. 26:21-34
Olshausen and Field (2000): Vision and the Coding of Natural Images. American Scientist. 88:238-245
Additional Reading:
Simoncelli, E.P., Olshausen, B. A.: Natural Image Statistics and Neural Representation. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2001. 24:1193-216
Simoncelli, E.P.: Vision and the statistics of the visual environment. Current Opinion in Neurobiology 2003, 13:144-149.
Motion perception begins already in area V1 by motion sensitive cells and then continues in the dorsal pathway in areas MT and MST.
Suggested Reading:Adelson, E. H., Bergen, J R. (1985): Spatiotemporal energy models for the perception of motion. Simoncelli, EP, Heeger, DJ (1998): A Model of Neuronal Responses in Visual Area MT. Vision Research, 38(5), 743-76.
Part III High-level Vision
High-level vision deals with questions of how we recognize objects or scenes and how we direct processing resources to particular aspects of visual scenes (visual attention).
Object recognition appears to be solved by a hierarchically organized system that progressively increases the complexity and invariance of feature detectors.
Suggested Reading:
Riesenhuber, M, Poggio, T (1999) Hierarchical models of object recognition in cortex, Nat. Neurosci. 2:1019-1025.
Serre, T, Wolf, L, Bileschi, S, Riesenhuber, M, Poggio, T (2007) Object recognition with cortex-like mechanisms. In: IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and MachineIntelligence, 29:411-426.
Additional Reading:
Kriegeskorte N. (2015) Deep Neural Networks: A New Framework for Modeling Biological Vision and Brain Information Processing. Annu Rev Vis Sci., 1:417-446.
Kravitz DJ, Saleem KS, Baker CI, Ungerleider LG, Mishkin M. (2013) The ventral visual pathway: an expanded neural framework for the processing of object quality. Trends Cogn Sci., 17:26-49.
Attention refers to mechanisms that allow the focusing of processing resources. Experimental observations, neural principles and system-level models of attention are described.
Suggested Reading:
Beuth, F., Hamker, F. H. (2015) A mechanistic cortical microcircuit of attention for amplification, normalization and suppression. Vision Research, 116:241-257.
Reynolds JH, Heeger DJ (2009) The normalization model of attention. Neuron 61: 168-185.
The perception of space is very crucial for systems that interact with the world. This lecture introduces to anatomical pathways of space perception. The primary focus is then directed to the problem of "Visual Stability", which deals with the question of why we perceive a stable environment regardless that each eye movement changes the content on the retina.
Suggested Reading:
Ziesche, A., Hamker, F.H. (2014) Brain circuits underlying visual stability across eye movements - converging evidence for a neuro-computational model of area LIP. Frontiers in Computational Neuroscience, 8(25), 1-15
Hamker, F. H., Zirnsak, M., Ziesche, A., Lappe, M. (2011) Computational models of spatial updating in peri-saccadic perception. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B (2011), 366: 554-571.
Husain, M., Nachev, P. (2006) Space and the parietal cortex. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 11:30-36.
Additional Material:
Jonikaitis_results_new.mp4, Jonikaitis_setup.mp4, PredictiveRemapping.mp4, predRemapping_setup.mp4
Part IV Cognition
Cognition deals with questions of how a system can learn and execute complex tasks and allow control over sensors and actions.
Suggested Reading:
Vitay, J., Fix, J., Beuth, F., Schroll, H., Hamker, F.H. (2009) Biological Models of Reinforcement Learning. Künstliche Intelligenz, 3:12-18.
Wiecki, T.V., Frank, M.J. (2010) Neurocomputational models of motor and cognitive deficits in Parkinson's disease. Prog. Brain Res. 183:275-297.
Suggested Reading:
Bird CM, Burges N (2008) The hippocampus and memory: insights from spatial processing. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 9:182‐194.
Lisman J, Redish, A.D. (2009) Prediction, sequences and the hippocampus. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B, 364:1193‐1201.
Suggested Reading:
Balleine, B. W., & O'Doherty, J. P. (2009). Human and rodent homologies in action control: Corticostriatal determinants of goal-directed and habitual action. Neuropsychopharmacology, 35:48‐69.
Doll, B. B., Simon, D. A., & Daw, N. D. (2012). The ubiquity of model-based reinforcement learning. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 22:1075‐1081
Exercises
| Instructions to set up python environment: Here | |
| Exercise I.1: Tutorial on the neuro-simulator ANNarchy | Files: exerciseI.1.zip |
| Exercise II.1: Gabor filters | Files: exerciseII.1.zip, solution
exerciseII.1_new.zip |
| Exercise II.2: Depth perception | Files: exerciseII.2.zip
exerciseII.2_new.zip |
| Exercise II.3: Efficient coding | Files: exerciseII3.zip |
| Exercise III.1: Object Recognition and HMAX, Serre et al. (2004) | Files: exerciseIII.1.zip |
| Exercise III.2: Normalization model of attention | Files: exerciseIII.2.zip |
| Exercise III.3: Visual attention and experimental data | Files: exerciseIII.3.zip |
| Exercise III.4: Space perception | Files: exerciseIII.4.zip |
| Exercise IV.1: Basal ganglia | Files: exerciseIV.1.zip |
| Exercise IV.2: Hippocampus | Files: exerciseIV.2.zip |