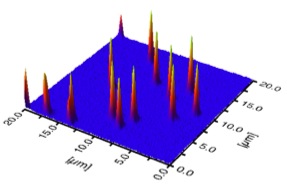
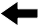
we apply a scanning version of photothermal lens spectroscopy. the heat deposition in the environment of an absorbing particle induces a refractive index change, which is deflecting a probe laser beam. this deflection is detected by a pinhole and a photodiode.
photothermal detection of single quantum objects


non-fluorescent objects are difficult to detect optically if their size is considerably smaller than the optical wavelength and scattering cross sections are small. However, if they absorb light which is then subsequently converted into heat, refractive index changes of the local environment of the absorbing species can be detected. this type of spectroscopy is termed photothermal spectrsocopy and allows access to non-fluorescent objects even in the fundamental limit of a single quantum object.
confocal photothermal image of gold nanoparticles embedded in a polymer film.