Robust Factor Graphs for Pose Graph SLAM
Motivation
 Current state of the art solutions of the SLAM problem are based on
efficient sparse optimization techniques and represent the
problem as probabilistic constraint graphs.
Current state of the art solutions of the SLAM problem are based on
efficient sparse optimization techniques and represent the
problem as probabilistic constraint graphs.
For example in pose graphs the nodes represent poses and the edges between them express spatial information (e.g. obtained from odometry) and information on loop closures. The task of constructing the graph is delegated to a front-end that has access to the available sensor information.
The optimizer, the so called back-end of the system, relies heavily on the topological correctness of the graph structure and is not robust against misplaced constraint edges. Especially edges representing false positive loop closures will lead to the divergence of current solvers.
Our solution

We developed a novel problem formulation that allows the back-end to change parts of the topological structure of the graph during the optimization process. The back-end can thereby discard loop closures and converge towards correct solutions even in the presence of false positive loop closures. This largely increases the overall robustness of the SLAM system and closes a gap between the sensor-driven front-end and the back-end optimizers.
We propose to augment the original optimization problem by a new set of hidden variables. These switch variables allow the optimizer to estimate the optimal graph topology and the optimal covariance for each potential outlier constraint. Despite the increased number of variables, the sparse structure of the problem is maintained, which allows efficient calculations.
Please see the publications below for further details.
Results on various datasets
For the evaluation we added false positive loop closures to several standard datasets that are commonly used in the SLAM community. These false positive loop closures were added following different policies to achieve a realistic distribution. Despite a vast number of false loop closure constraints, our proposed robust method is able to converge to a correct solution, discarding all outlier constraints.
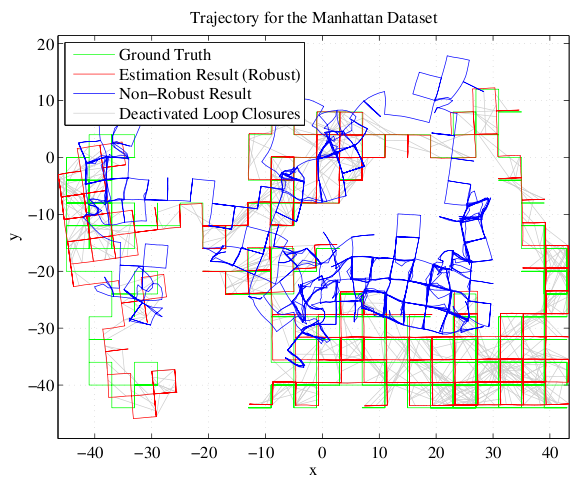
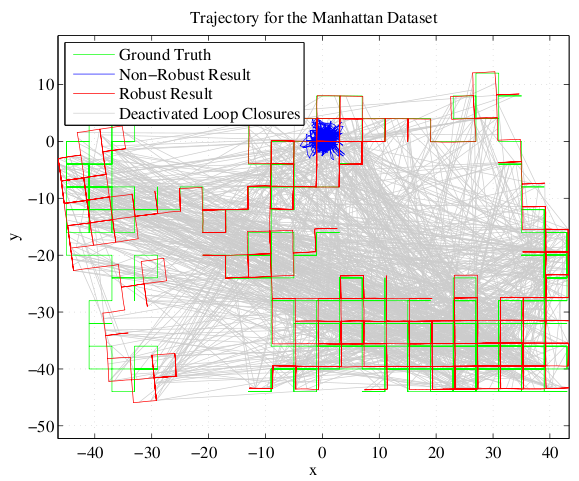
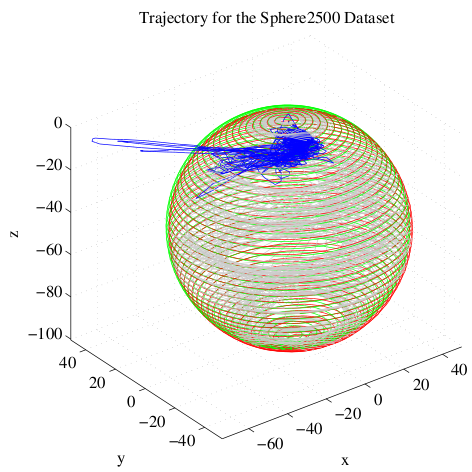
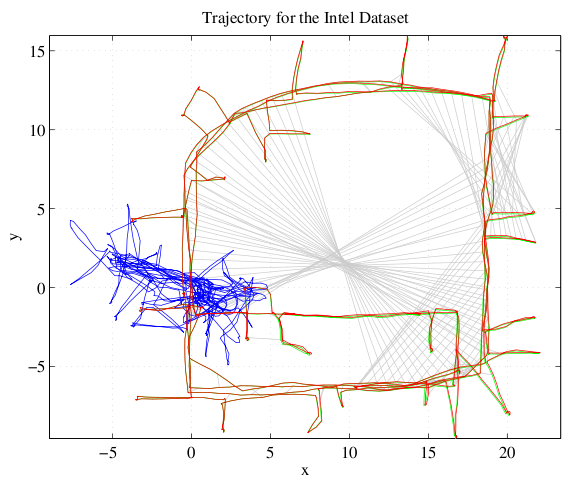
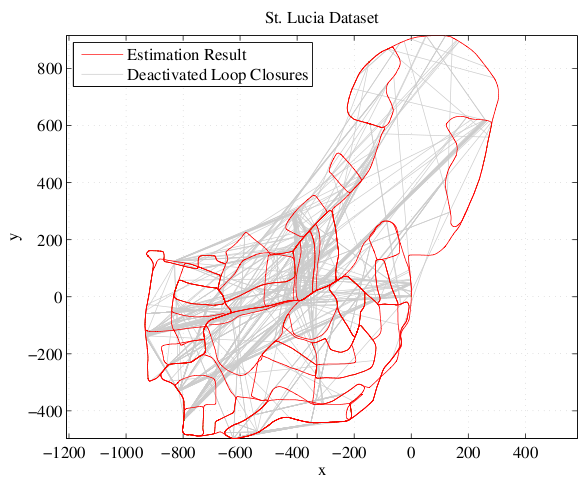
This works for a large real-world dataset as well. We tested it on the St. Lucia Dataset which covers 66 km of suburban roads. The only sensor information are the images of a webcam mounted on top of a car. The vehicle's ego-motion and the place recognition were performed using very simple methods (like BRIEF-Gist) on these images. Despite the large number of false positive loop closure detections caused by the simplistic place recognition module, the SLAM system is able to perform well and create a semi-metric map that is almost correct. (Thanks to Michael Milford for providing the dataset.)
Download the Source Code and Datasets
Vertigo: Versatile Extensions for Robust Inference using Graphical Models
Vertigo is an extension library for g2o and gtsam 2.0.
It provides a C++ implementation of the switchable constraints described in our publications (see below). This extension enables g2o or gtsam to solve pose graph SLAM problems in 2D and 3D despite a large number of false positive loop closure constraints.
In addition, a re-implementation of the max-mixture model described in (Olson and Agarwal, 2012) for g2o and gtsam is also contained.
Furthermore, Vertigo contains a number of standard pose graph SLAM datasets and a script to spoil them with false positive loop closure constraints. These datasets have been used in our evaluations. They can serve as a set of benchmark datasets for future developments in robust pose graph SLAM.
Download
- Vertigo is available at openslam.org
Publications
- (2013) Switchable Constraints vs. Max-Mixture Models vs. RRR -- A Comparison of three Approaches to Robust Pose Graph SLAM. In Proc. of Intl. Conf. on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). DOI: 10.1109/ICRA.2013.6631320
- (2012) Switchable Constraints for Robust Pose Graph SLAM. In Proc. of Intl. Conf. on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). DOI: 10.1109/IROS.2012.6385590
- (2012) Towards a Robust Back-End for Pose Graph SLAM. In Proc. of IEEE Intl. Conf. on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). DOI: 10.1109/ICRA.2012.6224709
- (2012) Robust Optimization for Simultaneous Localization and Mapping. Dissertation: Chemnitz University of Technology
We successfully applied our approach to robust optimization to the problem of multipath and NLOS mitigation in satellite-based localization. More details can be found here.
